
QUICK REFERENCER TDS HAND BOOK FOR DDOS FINANCIAL YEAR 2021-22
written by:
Anson Francis
Senior Accountant
Addl.Sub Treasury Manachira
Kozhikode
The Indian Income Tax Act provides for chargeability of tax on the total income of a person on an annual basis. Income Tax collected as four way

Tax Deducted at Source (TDS) -is a system introduced by Income Tax Department, where person responsible for making specified payments such as salary, commission, professional fees, interest, rent, etc. is liable to deduct a certain percentage of tax before making payment in full to the receiver of the payment. TDS is a form of collection of Income Tax.
India’s Dual income tax system introduced w.e.f 01.04.2020.

Budget 2020 introduces a new regime u/s 115BAC giving an option to individuals to pay income tax at lower rate.the new system is applicable w.e.f 1st Apr 2020.AY2021-22
The new tax regime removes to the claim for about 70 deductions, exemptions & housing loan interest(property loss).(if you have let out property you can claim a deduction for interest paid on the housing loan.
An employee can choose the new tax regime at the beginning of FY 2021-22 and intimate their DDOs. The employee cannot change their choice anytime during the financial year. In case an employee does not choose the new tax regime at the beginning of the financial year, the DDO will deduct tax TDS under the existing tax regime.
Available Exemptions in New Regime
- Conveyance/Transport- allowances in case of a specially-abled person.
- Conveyance allowance (PCA)received to meet the conveyance expenditure incurred. as part of the employment.
- Any compensation received to meet the cost of travel on tour or Transfer.
- Daily allowance received to meet the ordinary regular charges or expenditure you. incur on account of absence from his regular place of duty(Tour TA/Transfer TA/Daily Allowance).
No changes /No concession for Senior citizen/Super Senior Citizen in New Tax Regime(Taxable income Exceeding >5Lacks)

Rebate u/s 87A
The amount of rebate u/s87A FY 2021-22 (AY2022-23) has been kept unchanged under both old regime & New tax regime .Taxable income up to 5 lacks will get a tax rebate of Rs-12500/- or Equal to the amount of tax payable(Which ever is lower)
Education and Health Cess 4%
STRUCTURE OF INCOME AND TAX CALCULATION
As per the Section 14 Income Tax Act,1961, there are five main income tax heads for an individual. The computation of income tax is an important part and has to be calculated according to the income of a person. For a hassle-free calculation, the income has to be classified properly so that there is no confusion regarding the same. The government has classified the sources of income under separate heads and then the income tax is computed accordingly. The provisions and rules are according to the details mentioned in the Income Tax Act.
Head of Income
1)Income From salaries/pension
2)Income from House Property
3)Income From business or Profession
4)income From Capital Gain
5)Income From other Source
Old regime Calculation
1) Rate of Income Tax : Age below 60 Years
Upto Rs.2,50,000/- Nil
Rs.2,50,001/- to Rs.5,00,000/- 5%
Rs.5,00,001/- to Rs.10,00,000/- 20%
Rs.10,00,001/- and above– 30%
Eg.
(without cess)
Taxable Income 300000 – 0 (Rebate`12500)
Taxable Income 400000- 0 (Rebate`12500)
Taxable Income 500000- 0 (Rebate`12500)
Taxable Income 600000- 32500(12500+20000)
Taxable Income 1000000- 112500 (12500+100000)
Taxable Income 1100000 – 142500 (12500+100000+30000)
2) For Senior Citizens – Age above 60 years and below 80 years.
Up to Rs.3,00,000/- Nil
Rs.3,00,001/- to Rs.5,00,000/- 5%
Rs.50,0,001/to Rs.1000000/- 20%
Rs.1000001/- and above 30%
Eg.
(without cess)
Taxable Income 350000 – 0 (Rebate 12500)
Taxable Income 400000 – 0 (Rebate 12500)
Taxable Income 500000 – 0 (Rebate12500)
Taxable Income 600000 – 30000 (10000+20000)
Taxable Income 1000000 – 110000 (10000+ 100000)
Taxable Income 1100000 – 1400000 (10000+100000+30000)
3) Super Senior Citizens -Age above 80 Years
Up to Rs- 500000/- Nil
Rs. 500001 to Rs-1000000/- 20%
Rs.10,00,001/- and above 30%
Eg.
(without cess)
Taxable income 500000 – 0 (rebate 12500)
Taxable income 1000000 –100000
Taxable income 1100000 – 130000(100000+30000)
Gross Income Means
Salary /Pension (Not Include Family Pension Gratuity, Commutation ,Terminal Surrender of Earned Leave ,GPF closure etc…(For Govt Employees)
Allowance Exemption Means
HRA (Conditions based),Uniform Allowance ,Daily Allowance. etc..(HTA not Exempted(No Notified hilly areas in kerala state)
Other income Means
Income from House property, Profit from Business or profession, Capital Gain,FD int.,Family Pension(Less standard Deduction 15000/-) etc..)
Allowances Fully Taxable
- City Compensatory Allowance
- Fixed Medical Allowance
- Refreshment Allowance
- Rural Allowance
- Project Allowance
- Post mortem allowance
- Overtime allowance
- Any other Cash Allowance
- Conveyance Allowance
- Transport Allowance
- Hill Tract Allowance in kerala
- Sumptuary Allowance (Fully Taxable-judicial officers of District court)
Allowances Exempted
- Travelling Allowance
- Daily Allowance
- Uniform Allowance
- Helper allowance
- Children Education
- Allowance-up to 100/-per
month (Max-2 children) - Conveyance Allowance for physically
Disabled Employees –Max 1600/-month - Leave Travell Allowance(LTC)- Partially Exempted
- Sumptuary Allowance(fully Exempted-judicial officers of High court)
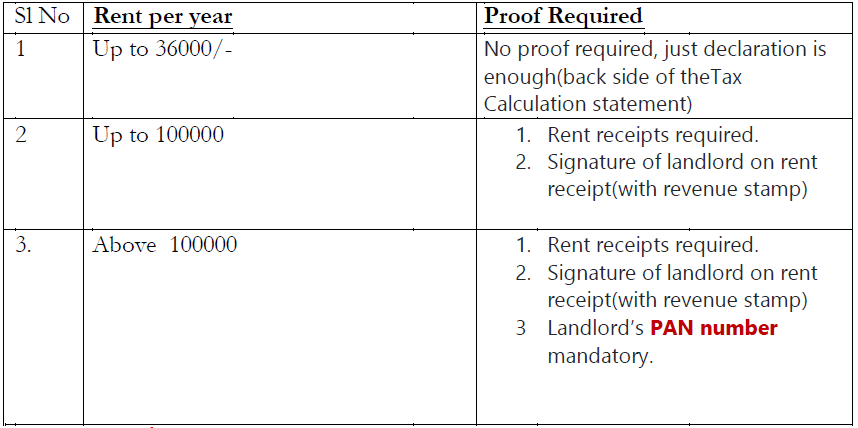
HRA (Section 10(13A)
An employee who is in receipt of House Rent Allowance can claim exemption, if he does not live in his own house, and pays rent in excess of 10% of Salary (Basic Pay+ DA) for his residential accommodation. Least of the following is allowed as Exemption
Small Eg:
PAY=50000; DA=10000; HRA=2000; Rent=7200;
Actual amount of HRA Received —->2000*12=24000/-
House Rent paid in excess of 10% of salary—->b) (7200*12)=86400-72000=14400
Amount of Exempted HRA =14400/- HRA chargeable to tax=9600/- (24000-14400)
Deduction under Chapter VI A
U/S-80C
Payment of insurance Premium –self,spouse or any child of individual Eg.LIC,SLI,GIS,Postal Life insurance,General public provident fund,public provident fund,NSC,Term deposit (5year) Sukanya samriddi account scheme..etc
LIC Premium issued before 01-04-2012 deduction up to 20% of the actual capital sum assured
LIC Premium issued After 01-04-2012 deduction up to 10% of the actual capital sum assured
Payment to notified annuity plan of LIC or any other insurer
Housing loan repayment(Loan taken for construction/purchase only.House should not be transferred for 5 years)
Subscription towards notified units of mutal fund eg.ELSS,Stamp duty,Registration duty and other expenses for the purchase of house property Tution fees-Full time education of any two children of the employee eg-full time education includes Play-School activities, Pre-Nursery and Nursery classes. Tution Fees paid to coaching centres not allowed as deduction Infra Structure development bonds of ICICI/IDBI/NABARD bonds.
U/S-80CCC-pension fund
Deduction in respect of Payment of premium for annuity plan of LIC or any other insurer. Deduction is available upto a maximum of Rs. 150,000/-.
The premium must be deposited to keep in force a contract for an annuity plan of the LIC or any other insurer for receiving pension from the fund.
U/S-80CCD(1)
Deduction for contribution in pension scheme notified by the Government to the extent of 10% of salary in case of employees and 10% of total income in case of others.(NPS
Employee contribution)- ,Employer(Govt) contribution not considered 80CCD(2)) Note- NPS Tier2 is fully Taxable
( The aggregate amount of deduction under section 80C, 80CCC and 80CCD(1)shall not exceed Rs. 1,50,000/-)
U/S-80CCD(1B)
Contribution to National Pension Scheme. The deduction is in addition to the maximum deduction of Rs. 1,50,000/- available under 80C, 80CCC and 80CCD(1).
Rs. 50,000,
Eg- Name X- GPF Contribution-130000/- ,NPS -30000/-
=130000(80C)+20000(80CCD(1))=150000/- (Max.150000/-) Addl. 80CCD(1B)=10000/-
U/S-80D

U/S80DD
Deduction in respect of maintenance including medical treatment of dependent who is a personwith disability.Rs.1.25lacks, (disability over 80%)severediability -Rs. 75,000 – others.The DDO has to allow deduction only if acertificate in form 10IA is furnished
U/S 80DDB
80DDB provides that an individual or a Hindu undivided family is eligible for deduction in respect of amount paid for medical treatment of certain specified diseases (cases of critical illness). 40,000/- or the amount actually paid, whichever is less.In case of senior citizen Rs, 1,00,000 or amount actually paid, whichever is less. Certificate in Form 10I is no longer required. The tax department has specified some details that the certificate must include. The certificate must have name and age of the patient, name of the disease or ailment, name, address, registration number and the qualification of the specialist issuing the prescription. If the patient is receiving the treatment in a government hospital, it should also have name and address of the government hospital.
U/S80E
The loan should be taken from any Bank / financial institution or any approved charitable institutions It should also be noted that if your loan tenure exceeds 8 years, then you cannot claim a deduction for the interest paid beyond 8 years.No limit (interest). no tax benefit for the principal part of the EMI.
U/S80EE
Section 80EE allows tax benefits for first time home buyers. An Income tax deduction can be claimed on your home loan interest towards your first house property. The deduction allowed under this section is for the interest paid on a home loan for up to a maximum of Rs 50,000 per financial year. You can continue to claim this deduction until you have fully repaid the loan
U/S80EEA
an individual can claim additional deduction of Rs 1.5 lakh on interest paid on home loan under the newly introduced section 80EEA subject to certain conditions. The Conditions are follows-
a) The loan must be taken between April 1,2019 and 31-mar-2020
b) Individual should not own any house on the date of sanctioning of loan
U/S80EEB
Additional income tax deduction of up to Rs. 1.5 lakhs is proposed on payment of interest on loan is taken to purchase electric vehicles
U/S80G
Eligible Donations upto either 100% or 50% with or without restriction eg..CMDRF,Balaswanthanam etc…Cash payment allowed upto 2000/-
U/S80GG
Do not receive HRA (House Rent Allowance) but pay rent, you can still get a tax deduction on the rent paid under Section 80 GG of the Income Tax Act, 1961. The
maximum deduction permitted under Section 80 GG is Rs 60,000 per annum (Rs 5,000 per month). You cannot get the benefit of this section if you (or your wife/minor child) own a house property. In order to claim the benefit of this section, you have to fill form
10 BA.
The deduction under Section 80GG is given to the least of the following
1.Total rent paid minus 10% of total income.
2.Rs 60,000 per year (Rs 5,000 per month).
3.25% of the adjusted gross total income
U/S80GGC
Deduction in respect of contributions made to political parties. The payment should be made any mode other than cash .The deductor cannot allow this claim as deduction for the purpose of tds
U/S80TTA
Interest on Saving accounts Max-10000/-Should be include the interest in gross total income-Then claim deduction of Rs-10000/- or actual interest whichever is less
U/S80TTB
Section 80TTB: Deduction for Senior Citizen [FY 2019-20] In budget 2019, the government has provided a big relief to our senior citizens (60 years or more) in form of a deduction of their interest income up to Rs.50,000/-(interest from FD,RD etc..)
U/S80U
This deduction is allowable for Individual with disability including blindness, mental retardation loss of voice, Autisum, cerebral palsy and multiple disability. A fixed deduction of Rs. 75,000 irrespective of amount paid is allowable. If the individual is a person with severe disability (disability over 80%) deduction is Rs. 1,25,000. Disability should be certified by a Neurologist /Paediatric Neurologist with MD or a Civil Surgeon / Chief Medical Officer of a Government Hospital. Form 10-IA should be furnished for Autism, cerebral palsy and multiple disability.